On the prevention of gynecological diseases.
As you know, these diseases are rare, but they do exist. Remember that poor-quality and non-nutritious feeding of females contributes to the occurrence of gynecological diseases. Rabbits must be kept in clean rooms with a good microclimate. It is also necessary to monitor the condition of the queens in the pre-breeding period and later. People say: “Cleanliness is the key to health.” The owner must maintain cleanliness and sanitary conditions at all times when keeping rabbits. Dust and the microflora present in it have a negative impact on animal health. Therefore, it is necessary to maintain sanitary order.
Disease prevention
To prevent the disease, special feeds with premixes containing coccidiostats are used.
Regular thorough disinfection of cells and equipment with special preparations is important.
Regular feeding of livestock with medicines in doses recommended by manufacturers is mandatory.
The breeder must:
- monitor the cleanliness of cages and enclosures;
- limit animal intake of protein foods;
- give complete nutrition, including coarse fiber.
If a disease is detected, the enclosures must be treated with an open fire and the equipment must be boiled. Destroy all items that cannot be processed.
The appearance of the disease is facilitated by crowded areas where animals are kept, untimely cleaning of the area, and accessibility for rodents or birds to enter cages.
The disease can occur at any time of the year, but the most striking manifestation is recorded in spring and summer
At what age should rabbits be treated for coccidiosis?
For the purpose of prevention, young animals begin to be given drugs from 2-3 weeks of age, while they are with the female.
It is obligatory to solder it at the moment of leaving the rabbit, as well as before reaching the age of two months.
Cleaning the rabbitry
General cleaning is carried out every ten days. This day is usually called sanitary day. On a sanitary day, floors, walls, ceilings, and work equipment are treated with a 3% solution of soda ash; You can also use boiling water. Work equipment is processed in a bucket.
1-1.5 hours after the initial treatment, the entire room is thoroughly cleaned. Walls and ceilings are washed with a brush, and cages and food storage areas are thoroughly cleaned. Existing cracks and potholes in floors and walls are carefully sealed. Metal meshes and other objects can be burned with a blowtorch, while observing safety precautions.
In summer, be sure to treat the premises against flies and blood-sucking insects!
If rodents are present, they are destroyed. They carry out repairs to feeders, drinking bowls, and floors in cages. At the end of the sanitary measures, all items that were used in the work (brooms, shovels, scrapers, etc.) are cleaned of dirt, washed with hot water and a disinfectant solution. Activities carried out daily: removing manure, cleaning feeders and drinkers, monitoring the health of rabbits, examining rabbits in the nest and the mammary glands of females within 5-6 days after birth.
Pathways of transmission and developmental features of the pathogen
The disease in rabbits is caused by several types of coccidia. One of them - Eimeria stiedae - is localized in the liver, the remaining varieties live on the intestinal mucosa.
Rabbits for a long time (according to many experts throughout their lives) can be carriers of coccidia in the absence of any symptoms. Infected individuals, as well as other rodents, birds, and flies serve as a constant source of spread of the infestation, releasing oocysts (eggs) of parasites along with feces. They are very stable in the external environment and can survive for more than a year on the surfaces of cages, feeders and drinking bowls, in bedding and waste products of animals. Exacerbations of the disease are more often observed in the spring-summer period in young animals aged 1-3 months, which become infected when sucking mother's milk (a carrier of parasites) or a sudden change in feed after weaning.
A protozoan unicellular parasite that causes coccidiosis in animals
The life cycle of the parasite consists of several stages. Oocysts that enter the animal’s body develop from 4 days to 2 weeks and, under the influence of active media in the gastrointestinal tract (GIT), their membranes are destroyed. The released virulent spores actively invade the liver or intestinal tissue and in a short time turn into mature gametes capable of fertilization and the production of new oocysts.
The clinical manifestation of the disease is facilitated by viral and bacterial infections, helminthic infestations, which reduce the protective functions of the gastrointestinal tract and the animal’s immunity.
Prevention of diseases in rabbit farming
The main prevention of diseases in rabbits is vaccination. Preventive vaccination must be carried out in a timely manner. For a number of infectious diseases in rabbits, it is impossible to do without vaccination.
Vaccination is a preventive vaccination of rabbits with a vaccine to create immunity to an infectious disease. As a result of vaccination, rabbits become immune to the disease (immunity).
Single or double (depending on the vaccine) vaccination is carried out. It is advisable to carry out helminthization before vaccination. You need to know that it is not recommended to vaccinate sick rabbits. The owner can carry out the vaccination himself. If there is the slightest complication after vaccination, you should call a veterinarian.
Feed purchased for feeding rabbits is first fed to several rabbits. If no health problems are found, then they feed it to the entire livestock. Purchased feed must have a veterinary quality certificate and must be tested for the presence of diseases. To prevent gastrointestinal diseases, it is recommended to give biomycin to rabbits at the age of 3 weeks: before weaning - 0.5 milligrams, after weaning and up to 100 days - 1 milligram per individual.
If there is a dog in the farm yard, then it must be treated against worms.
Newly acquired rabbits are kept for 10-15 days in an isolated room, that is, they are quarantined and monitored. Such an event has an important role in the prevention of rabbit diseases.
Quarantine is the temporary keeping of rabbits in isolated conditions. Quarantine measures are carried out to prevent further spread of infection from the source of its occurrence. Quarantine is also used for newly acquired rabbits. It is necessary to protect the main herd from the occurrence of diseases. There is a good Russian proverb: “God protects those who are careful.” Quarantine time is 35-40 days. Newly acquired rabbits are examined and kept in separate cages. In this case, the owner must wear a robe and shoes that can be easily disinfected. When servicing quarantine rabbits, individual care items are used (combs, dishes, broom, etc.). During this time, it is determined whether the rabbit is sick or not. If no changes are found in the rabbit during quarantine, it is “enrolled” into the general herd. In recent years, laboratory testing of rabbit blood for nutrients has been introduced in rabbit farming. If you have such an opportunity, you must use it.
Events held during quarantine.
- The export and import of new rabbits and feed into the farm is prohibited.
- The room where quarantine rabbits are kept must be isolated.
- Access to the premises is permitted only to service personnel.
- It is prohibited to keep quarantine rabbits together with other pets.
- When entering a quarantine room, it is advisable to place a disinfectant mat.
- When servicing quarantine rabbits, have separate special clothing and equipment.
Is it possible to eat rabbit meat that has coccidiosis?
Rabbit coccidiosis is not dangerous to humans. You can eat meat without fear, you just need to dispose of the affected internal organs. Temperatures above 100 °C are lethal for coccidia, so after heat treatment the meat becomes completely harmless. However, many people, having seen enough of sick rabbits, disdain to eat meat and throw it away.
The skins of sick rabbits will have to be thrown away. An infected animal's fur becomes dull and crumpled; it is useless to use in furriery.
Disinfection
Disinfection is measures aimed at destroying pathogens of infectious diseases in the external environment. The objects of disinfection can be premises, manure, clothing. Disinfection destroys microorganisms along the route of transmission from the source of infection to the susceptible animal.
Disinfection is divided into biological, physical, chemical. An example of biological disinfection is the disinfection of water pipes and reservoirs from which water is taken for rabbits. For physical disinfection, high temperature, boiling, fire, bactericidal lamps, etc. are used.
In chemical disinfection, chemicals (caustic soda, formaldehyde) are used for disinfection. Disinfection can be carried out by irrigation, aerosols or gases. Disinfection by irrigation. With this method, disinfectants are used: 10% sodium hydroxide solution, 1% formaldehyde solution, bleach solution and others. The temperature of the disinfectant solution should be 70-80 °C. Chlorine-containing solutions and formaldehyde solutions cannot be heated to this temperature. The aerosol method is a disinfection method in which a solution in the form of particles 10-15 microns in size is applied to the surface to be cleaned. Aerosols are sprayed using special devices. Aerosol disinfection can also be carried out in the presence of rabbits. Currently, aerosol disinfection using a non-hardware method has been developed. Disinfection can also be carried out by gas treatment.
Disinfection can also be preventive, current, final:
- Preventive disinfection is carried out once or twice a month. For this, a 2% NaOH solution or a clarified solution of bleach is most often used. The temperature of these solutions should not be lower than 70 °C.
- Current disinfection is carried out taking into account the infectious agent.
- Final disinfection is carried out before lifting quarantine.
Wooden cages, care items, walls, floors, and ceilings of the room can be irrigated with disinfectant solutions from any available sprayers. Easily accessible places can be scalded with boiling water or boiling lye. You can successfully use a solution of freshly slaked lime. A special requirement is to observe safety precautions when performing this work.
The fire burning method can be used to disinfect metal cages and other ancillary equipment. To do this, use a blowtorch with great fire safety precautions. Many practicing rabbit breeders recommend making cages for young animals from auxiliary mesh, using a continuous covering only for the ceiling. Young animals are kept in such cages for 0.5-1 year, and then the cages are disassembled, thoroughly disinfected and used again. Collapsible cages are easier to disinfect, especially in relation to coccidia, which are not so easy to combat. This approach provides reliable prevention against infectious diseases.
Remember! The quality of disinfection depends on the conscientiousness of following disinfection instructions.
Disinfection mat. It is installed at the entrance to the rabbitry and serves to disinfect the feet of the entering owner. The rug is made from a wooden or metal quadrangle. Sawdust or perlon is poured inside, which is moistened with a disinfectant solution. The average size of the rug is 50x50x3. Disinfection mats are a means of preventing infectious diseases in rabbits.
The quality of disinfection is determined in the laboratory. 2-3 hours after disinfection, samples are taken for laboratory testing.
The laboratory gives an opinion on the quality of the disinfection performed.
Some disinfectants
- Bleach is an effective disinfectant that is successfully used in rabbit farming. It is a white or gray powder with a chlorine smell. Chlorine is contained in lime up to 40%. Chlorine is stored in packages in a cool, dry place. To disinfect floors, walls, ceilings, cages, equipment, 5-, 10- and 20% aqueous solutions are used. Rabbit manure is disinfected with bleach by sprinkling the powder at the rate of 100 grams per 1 cubic meter. Bleach reacts with metal. Therefore, it is not recommended to disinfect metal care items. When working with bleach, you must observe personal safety precautions!
- Formalin is a 40% solution of formaldehyde. It is a colorless liquid with a pungent characteristic odor. The product has a good bactericidal effect and is used as a disinfectant. They use it to disinfect the room where food and cages are stored. Use a 1-3% solution. When using formalin, precautions must be taken. Formaldehyde is toxic. It has a negative effect on vision, respiratory organs and skin.
- Caustic soda (sodium hydroxide). In practice, sodium hydroxide is called caustic soda, caustic soda, caustic alkali. When working with sodium hydroxide, you must be careful. If it gets on mucous membranes or skin, there may be burns. When working, you must use goggles, gloves, and aprons. For preventive disinfection, use a 1-2% solution of caustic soda. A solution of sodium hydroxide at a temperature of more than 70 °C has the best bactericidal effect.
- Cool boiling water. This is water with a temperature of at least 90 °C. In rabbit farming, boiling water is successfully used as a disinfectant.
- Chloramine is a powder with a chlorine odor. It dissolves well in water. For disinfection, use a solution heated to 60 °C. Chloramine contains up to 30% chlorine. Chloramine disinfects workwear well.
- Potassium permanganate (potassium permanganate, potassium permanganate). This product is used for external disinfection of rabbits for various bruises and injuries. To do this, use a solution of potassium permanganate in a concentration of 0.01-0.5%. A solution of potassium permanganate can be used as a room deodorizer.
- Carbolic acid is a clear liquid with a peculiar odor. It has strong bactericidal and antiparasitic properties. Carbolic acid is used to disinfect premises, care items, workwear, etc. The acid is used externally in the form of a 3-5% solution. The acid kills lice and ticks in 2-8 minutes (2% solution), in 1-2 minutes (5% solution). When carrying out disinfection with carbolic acid, precautions must be taken.
Disinsection in rabbit farming
Disinsection - destruction of harmful insects.
Disinsection can be mechanical, physical, chemical and biological.
- A mechanical way to control insects is to catch them using sticky paper;
- The physical method is the use of fire, dry heat, boiling water, etc.;
- The biological method includes the destruction of insects by their natural enemies.
The most effective method of controlling insects is the chemical method (insecticides).
Fighting flies. Preventive measures:
- Avoid accumulation of manure near the premises;
- Carry out mechanical cleaning of floors, cages, passages, feeders daily;
- Avoid loss of feed during distribution, especially boiled mixtures;
- On sanitary days, carefully clean corners and hard-to-reach places where dust and cobwebs can accumulate;
- Avoid long-term storage of root and tuber crops.
Exterminatory measures. To exterminate insects, water emulsions are used:
- To exterminate larvae and pupae - 0.33% karbofos, 0.2% chlorophos, etc.;
- To exterminate winged forms - a 0.5% solution of chlorophos and a 0.5% solution of soda ash, an aerosol of chlorophos and sodium hydroxide and others.
Deworming is the destruction of helminths at all stages of their development and in all their habitats. There are forced, preventive, preimaginal and diagnostic deworming. Forced treatment of rabbits is carried out in case of illness. Preventive – in order to prevent infectious diseases. Preimaginal helminthization is carried out so that there is no release of larvae and eggs from the rabbit’s body. Helminths are killed in the animal's body when they have not reached sexual maturity.
Disinfestation is the elimination of pathogens of invasive diseases (coccidia, eggs and larvae of helminths, etc.) in the external environment.
Decontamination is an event aimed at destroying parasitic mites in animal premises, pastures, etc.
Symptoms of coccidiosis in a rabbit
After infection, rabbits may not show any obvious symptoms of the disease for quite a long time. Only after rapid insemination and the spread of parasites throughout the body of the eared parasite do the first signs of the disease appear.
The severity of the disease is proportional to the number of coccidia - the more there are in the rabbit’s body, the brighter the picture of the disease becomes. Symptoms depend on the form of the lesion - intestinal, hepatic, mixed.
It is worth remembering about latent carriage, when a rabbit is a carrier of the pathogen, but at the same time does not have any symptoms. In this case, oocysts (eggs) will constantly enter the external environment, which will cause infection of a healthy tribe. To avoid possible carriage, it is recommended to keep rabbits in comfortable conditions and carry out timely prevention of infections.
Symptoms of the intestinal form
Intestinal coccidiosis is the most dangerous type of disease with a rather rapid course and pronounced symptoms:
- The appearance of diarrhea, which alternates with constipation.
- A lot of mucus with blood is visually detected in the stool.
- The animal's body temperature is very high.
- There is noticeable swelling of the abdominal cavity, but the stomach sags.
- The appetite decreases or the animal completely refuses to eat.
- The growth of the body stops.
- Mucus and pus may be discharged from the nose and eyes.
- The coat becomes faded.
- Convulsions are observed before the death of the rabbit.
If left untreated, the rabbit dies within 10-14 days.
Symptoms of the liver form
Hepatic coccidiosis has a latent course (symptoms increase up to 2 months). The symptoms are the same as for the intestinal form. But at the same time, the sclera of the animals’ eyes turn yellow. This form of the disease is treatable and has a favorable outcome.
However, this form of the disease easily becomes chronic, and the animal becomes dangerous to others. To prevent the spread of infection, the infected animal is housed separately until complete recovery or death (in the event of a repeated exacerbation of the disease, death is inevitable).
The occurrence of mixed liver and intestinal symptoms in one rabbit clearly leads to death. But at the same time, the animal becomes exhausted very quickly. Single convulsions of the back, paws, and neck are noticeable, which signal impending death. The duration of coccidiosis with a mixed course is up to 3.5 months.
The final diagnosis is made after an autopsy, microscopy of stool and based on symptoms. Under a microscope, coccidia eggs are found in the stool.
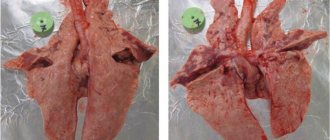
Signs in pathological anatomy
The diagnosis of coccidiosis can be fully confirmed after the death of the rabbit.
At the autopsy it is noted:
- The intestinal mucosa is swollen, red, with a white coating.
- White nodules with a cheesy content on the mucous membranes and liver are visually detected.
- The bile ducts are greatly dilated.
Deratization
Deratization - extermination of rodents. Deratization can be preventive or exterminatory. The rodent family (rat, mouse and similar pests) are the main carriers of diseases.
Preventive measures include constant and thorough removal of manure and proper storage of feed. In order to prevent rodents in rooms where rabbits are kept, it is necessary to maintain sanitary order, do not throw leftover food on the floor, do not clutter corners and other places convenient for rodents to nest; windows and ventilation pipes should be covered with mesh. Extermination measures are carried out by biological, mechanical, chemical and other methods:
- Biological method - the use of natural enemies of rodents (dog, hedgehog, cat).
- The mechanical method is to catch rodents using special traps and traps. Among rabbit breeders there is experience in catching mice in a glass milk bottle: the neck of the bottle is lubricated with oil. The mouse, like all living creatures, is very curious. She, examining the neck, slips and falls to the bottom. You can exterminate rodents using a mixture of flour and alabaster. At the same time, there should be water nearby. Rats and mice die after eating the bait and drinking water, as the alabaster in the intestines hardens.
- The method of pollination is the use of poisons in the form of dusting, dusting in places where rodents are concentrated, and on their routes of movement.
- The gassing method is the use of aerosols of poisons in enclosed spaces.
- The bait method is the use of various baits with the addition of poisons. The peculiarity of this method is that the bait must be placed in places inaccessible to rabbits.
- Folk method - branches of black elderberry and wild rosemary are used to control rodents. These branches repel rodents, and they do not settle indoors. The branches are laid out in the rabbitry in different places.
Comments:
Expand comments
Is coccidiosis transmitted from rabbits to humans?
It is important that coccidiosis in rabbits is practically not dangerous to humans. Even eating the meat of infected animals does not harm people, but eating liver should be avoided. Before disposal, damaged organs are poured with boiling water for disinfection (parasites die at high temperatures) so that oocytes do not constantly circulate throughout the farm. The skins of slaughtered rodents are used for their intended purpose, although they do not receive the first quality category. Cats, dogs, ducks, chickens have their own forms of oocytes, and coccidiosis in rabbits is not dangerous for them, as for people.