Home / Eco life / Village life / Farming / Poultry farming / Chickens / Diseases
Back
Published: 07/24/2017
Reading time: 8 min
0
2716
Chickens, like humans and most domestic pets, fall prey to various parasites.
This causes losses to the farmer and may even pose a risk to his health.
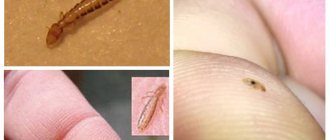
- External parasites: Downy lice or chicken lice
- Red chicken mite
- Syringophilosis or feather scabies
- Acariform mite
- Bedbugs
- Symptoms
Causes of infection
Adults are able to develop immunity to some types of helminths. Young animals are most susceptible to disease.
Common factors for the appearance of parasitic insects in chickens:
- dirty water;
- high indoor humidity;
- the flooring is rarely changed;
- the food is old and of poor quality;
- there are rodents in the chicken coop;
- birds eating slugs and earthworms;
- purchase of infected young animals.
Poultry can be infected by wild birds that fly in to eat from chicken feeders. The infection can also be brought by the person himself - on shoes, clothes and hands after working in the garden.
Signs of skin parasites
The first sign of failure is decreased productivity. In addition, it is worth paying attention to other factors:
- A change in the bird's behavior, accompanied by plucking and pecking of feathers.
- Increased feed intake.
- Sudden loss of feathers, partial baldness.
- Damage to the skin, its peeling, the appearance of traces of blood on the earrings and comb.
- If the parasites reach the eyes, lacrimation begins, sometimes purulent discharge due to the development of conjunctivitis.
- The feathers are damaged and there are visible holes in them.
Many parasites are afraid of light, so they hide under their wings or look for another place with a thick layer of fluff. To see them, you need to take the bird out into the sun or shine a lamp on it.
Be sure to check perches, bedding, walls and floors.
You need to get rid of parasites as quickly as possible, since they lay a large number of eggs, which is why the number of parasites grows exponentially.
External parasites
External parasites are divided into two types: mites (arachnids) and bedbugs, feather eaters, lice eaters (insects). The methods of reproduction and life cycle of insects are different, but the means of destruction are the same. This causes difficulties in the fight against parasitic organisms in birds.
Interesting! Lice and fleas do not live on chickens; they are confused with feather eaters.
Peregrines and lice eaters
The beetle does not drink blood; it feeds on feathers and secretions from wounds on the body. The parasite causes severe itching in the bird. It is difficult to notice, it camouflages itself with the color of the feathers and becomes invisible. You can detect insects using a lamp, pointing it at the bird's plumage. The lice eaters will crawl out in the warmth and become more noticeable. They live their entire lives on the host’s body; in the external environment they die within a week.
Chicken lice have no wings, their flat, elongated body is brown in color. The head with antennae is larger than the body. Insects have a jaw. Body length is from 1 to 2 mm.
One pair of lice eaters produces up to 90 thousand oval eggs (0.5-1.5 mm) during its life; the female glues them to the down or body of the chicken. The eggs take about a month to develop, it all depends on the air temperature and humidity of the room. After 12-14 days, larvae similar to their parents appear. They molt three times and become adults.
Symptoms of infection
The main signs of the presence of beetles:
- There are small holes near the base of the feathers;
- chickens become restless and peck themselves;
- feathers fall out;
- holes in fallen feathers;
- inflamed skin;
- weight loss;
- the number of eggs laid decreases;
- young animals do not grow;
- alopecia.
Bedbugs
Small insects cause suffering to chickens due to numerous bites. They drink blood from birds and animals. Reproduction occurs only after the female is saturated. Bedbugs can carry plague and fever. They attack at night and crawl into crevices in the morning. Bedbugs have a flattened body, brown in color, 1-2 mm in length.
Symptoms:
- the bird often itches with its beak;
- red bite wounds are visible on the body;
- feathers do not shine, appearance deteriorates;
- chickens begin to get sick, their immunity is weakened.
Ticks
Chicken mite 3/4 mm long, gray in color. It turns red-brown after being saturated with blood. Ticks feed on areas of the skin where capillaries are located close to the surface - eyes, chest, legs. Arachnids carry many dangerous diseases that can kill chickens.
They breed from May to mid-autumn. They are most active on warm days after rains. They can go without food for six months, hibernating. Parasites feed only on fresh blood, they inject toxins that do not allow wounds to heal, they bleed all the time.
Consequences: arachnids lead to anemia in birds, egg production decreases. Pigeon, bed, scabies, ixodid and subcutaneous mites can also bite birds. The latter constantly live under the skin of the chicken.
What kind of parasites do chickens have?
Chicken parasites can be internal or external.
External (external)
External parasites are small insects that live on the surface of the skin of chickens and in their feathers. In the process of their life, they cause significant harm to the health of birds. They:
- cause severe itching, which irritates the chicken, makes it aggressive , she has a tendency to clean her feathers too often, which leads to their loss;
- are carriers of infection.
A bird suffering from an invasion of parasites loses weight and its egg production decreases.
Chicken mite: diseases caused by the parasite
Read
Chicken lice: description of parasites and diseases they cause
Look
Chicken bugs are parasites that are carriers of dangerous diseases.
More details
How to get rid of feather eaters in chickens at home?
Further
Domestic
There are a huge number of varieties of internal parasites that can take up residence in a chicken’s body.
The activities of many of them can cause severe harm to the health of the bird, including death. The danger also lies in the possibility of human infection.
Roundworms (helminths) that cause various diseases
Worms
The most common parasitic disease of birds of the order Gallinae
Ascariasis
Parasitic disease of chickens caused by helminths
Syngamosis
Internal parasites
There are a large number of helminths that settle in the internal organs of chickens. Basically, chickens swallow larvae or eggs during free range. But dirty chicken coops and aviaries also contribute to the infection of birds.
Severe infestation with worms leads to the death of individual individuals. The larvae of some parasites can penetrate eggs. Eating raw eggs can become infected with helminths.
Type of worms:
- pinworms;
- roundworms;
- threadworms and tapeworms;
- histomonas;
- flat fluke;
- coccidia;
- heterakis;
- amidostomy.
When cutting a carcass, long worms can be seen in the intestines with the naked eye. The main signs of the presence of helminths in chickens:
- lethargy;
- refusal of food;
- convulsions;
- liquid droppings;
- weight loss;
- pallor of the comb;
- the number of eggs laid decreases, the shell becomes thin;
- apathy;
- paralysis.
Attention!
To diagnose helminthiasis, bird droppings are taken to a veterinary hospital.
Symptoms of appearance
The presence of a parasite can be determined by the way a bird behaves. The appearance of periodontal beetles will certainly make itself felt with a number of signs that have clear differences from other diseases:
- the bird is constantly itching and trying to pull out feathers;
- Baldness is observed in places, and holes form where feathers have fallen out;
- the plumage has damage at the base;
- the birds are very nervous, constantly cleaning their plumage;
- the growth of young individuals slows down, adult chickens slowly gain weight as they lose their appetite;
- the chickens stop laying eggs.
We recommend reading: Mandatory vaccinations
If you do not pay attention to the abnormal behavior of birds for a long time, this can lead to a decrease in their productivity. In addition, laying hens, when pecking at the skin, form wounds that fester over time.
Pus and inflammation in wounds are very dangerous. If there is no treatment and delay in getting rid of parasites, this can lead to the death of the laying hen.
Parasitic diseases
Parasitic diseases occur as a result of the presence of parasites on the body or internal organs of chickens. When one individual is infected, the disease can spread to the entire chicken coop. Not only the birds will suffer, but also the person who cares for them. After all, some diseases are transmitted from birds to humans. The main thing is to identify the problem in a timely manner and begin treatment.
Syringophilosis
Feather mange is caused by a mite that penetrates deeply into the base of the feather and becomes parasitic. The disease appears more often during warm periods. A healthy individual becomes infected from a sick chicken through the slit-like channel of the feather. Incubation time is 80-90 days. Scabies affects individuals 5-6 months old.
Signs:
- feathers break and fall out;
- a chicken pecks its own body;
- the skin turns red and inflamed;
- the disease spreads to areas of the back;
- earrings and comb turn pale;
- anemia;
- decreased productivity.
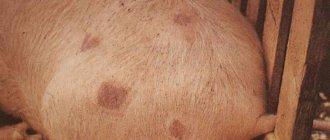
Knemidocoptosis
Roosters get sick more often than chickens. The acariform mite lives on the paws under the skin. It feeds on skin particles and lymphatic fluid. The skin thickens and turns white, and bumps appear. The disease is popularly called “calcareous foot.” Advanced disease leads to necrosis of the fingers. The tick can also infect the neck and wings.
Capillariasis
The causative agent is threadworms that live in the intestines. The last stage of the disease cannot be treated, the individual dies. The disease causes lethargy, developmental delays, and refusal to eat.
Ascariasis
Poultry are infected with roundworms when a chicken ingests helminth eggs. They settle in the intestinal tract. With the disease, the number of eggs laid decreases, exhaustion occurs, and appetite decreases.
Syngamosis
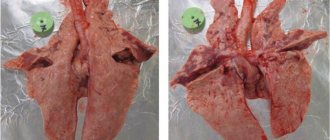
Singams attack the respiratory system. The chicken wheezes, refuses to eat, and loses weight.
Cestodosis
The disease is caused by tapeworms. They inhabit the stomach and intestines. The owner of the worms loses his appetite, becomes weak and lethargic, and experiences convulsions.
Interesting!
One female helminth hatches up to 50 million eggs per year. The taste of chicken meat deteriorates if the chicken is contaminated.
Prostagonymosis
The flat fluke lives in the cecum and rectum, sometimes in the oviduct. The eggshell becomes thinner or absent altogether. The chicken's belly swells, weakness.
Histomoniasis
Histomonas parasitize the liver or cecum. The birds develop apathy and rarely have yellow stools.
Heteracidosis
Heterakis are located in the cecum. There is a loss of strength, refusal to feed, diarrhea, and decreased egg production.
Amidostomiasis
Amidostomas live in the stomach, they affect the cuticles of the muscular section. The chicken refuses to eat, apathy occurs, and the young grow poorly.
Coccidiosis
Coccidia live in bird livers. Severe diarrhea occurs, weight decreases, and hens stop laying eggs.
Symptoms and types of worms
Symptoms characteristic of each disease are presented in the table:
| Disease | Symptoms |
Ascariasis - caused by roundworms called roundworms, which infect the intestines and can migrate through the circulatory system throughout the body. | Loss of appetite, drop in egg production up to its complete loss, convulsive states, paralysis |
Capillariasis is a pathology caused by threadworms that parasitize the intestines. | Complete loss of appetite, lethargy, developmental delay in chickens |
Syngamosis is caused by roundworms that parasitize the respiratory system. | Rapid exhaustion, wheezing, complete refusal to eat, loss of productivity |
Cestodosis - occurs due to tapeworms that parasitize the gastrointestinal tract. | Decreased appetite, severe weakness, seizures |
Histomoniasis – the causative agent of the disease is histomonas. The disease affects the cecum and liver. | Diarrhea with green or yellow droppings, severe lethargy |
Prostagonymosis - caused by a flat fluke that parasitizes the oviduct, cecum and rectum. | The bird's egg shells become thinner or completely lost, the belly becomes swollen and full, and a rapidly developing loss of strength is observed. |
Heteracidosis - provoked by nematodes that penetrate the cecum. | The bird loses its appetite, experiences weakness, suffers from diarrhea, and quickly loses productivity |
Amidostomiasis is caused by Amidostoma roundworms that infect the stomach. | Apathy and complete refusal to eat are the main manifestations in an adult; insufficiently rapid growth in young animals |
Common symptoms of the disease in chickens are an unkempt, sick appearance, blueness of the comb, and the presence of worms and their eggs in the droppings.
The parasites that inhabit the oviduct infect the eggs, causing their shells to become thinner and lumps of unknown nature to be found inside.
Occasionally, the parasites turn out to be especially large - then they become visible in the egg without optical magnification.
How to determine the presence of worms?
The presence of parasites in the body of a feathered pet can be assumed based on the signs that manifest helminthiasis.
An accurate diagnosis without an autopsy is only possible through laboratory examination of droppings and secretions (if any) from the beak and nose of the chicken.
Usually, careful attention to the bird helps not to miss the appearance of a problem, when the owner immediately pays attention to the violation of the pet’s condition.
When helminthiasis is detected at the beginning of infection, treatment is easy. Severe helminthic infestation can rarely be fully cured - chickens die in most cases.
A chicken can develop worms from the moment it starts going outside and pecking at grass and worms.
Treatment
Chicken lice are destroyed using modern medicines intended for animals. When using, take into account the weight of the chicken. If the ampoule is designed for 10 kg of weight, then 5-6 laying hens are treated with it. If there are a lot of birds, then aerosols are used.
Fighting chicken lice
Spray the bird with insecticides. The substance is diluted strictly according to the instructions and sprayed evenly on the feathers and body from a regular sprayer. Powdered preparations are also used; they are rubbed into the skin of each chicken. The medicine should not get into the eyes and nose. It is better to do this in the evening, when the family is on its roost.
The feather eaters are poisoned twice, the second time after 10-12 days. Insecticides do not kill lice eggs; you need to wait until the insects appear and re-treat.
Preparations:
- entobacterin 2%;
- cyodrine 0.25%;
- dibromine 0.05%;
- thuringin 5%;
- permethrin 0.5%;
- neostomozan, butox – 2 ml per 2 liters of water;
- pyrethrum;
- dicrelease 0.7%;
- Sevin 7% – 15 g of powder per head;
- deltamethrin;
- Ecofleece aerosol.
Medicines are purchased at veterinary institutions or pharmacies. It is better not to use chlorine-based products; it can accumulate in eggs and meat.
Treatment for ticks
The body of the bird is lubricated with vegetable oil. The tick cannot breathe, crawls out or dies. Wounds are treated with any antiseptic - hydrogen peroxide, iodine, chlorhexidine. The chickens are moved to a new place, and the chicken coop is treated with aerosols.
Powders are sprinkled on the feathers and body. Preparations:
- Sevin – 15 g of substance per individual;
- Pyrethrum;
- Peremethrin EU;
- Ecofleece.
Fighting bedbugs
Sand and ash are mixed 1:1 in a basin. They put it in a chicken shelter and the chickens bathe in this mixture. It should not get wet; it is changed every day. After 8-10 days, the procedure is repeated to kill the offspring of bedbugs emerging from the eggs. The floors and walls are doused with boiling water and a blowtorch is used.
Medicines Inkur 2%, Chlorophos 1% (200 g per bucket of water), all chickens are bathed in the solution.
Treatment of helminthic infestations
You may be interested in: How to make an automatic feeder for chickens How to treat coccidiosis in broilers at home Diarrhea in broilers: causes and treatment at home
Drugs that act on helminths are sold both in animal pharmacies and in regular pharmacies.
Preparations:
- Piperazine;
- Phenothiazine;
- Fenbendazole;
- Flubenvet;
- Febantel;
- iodide solution is diluted 1:1000;
- Hygromycin;
- Levamisole;
- Filixan, Fikasin;
- Cocciditis;
- Avatek;
- Rigecostat;
- Furazolidone;
- Biomycin;
- Enteroseptol;
- Trichopolum;
Any medicine must be given according to the instructions. If the tablets are intended for an animal or a person, you need to consult a veterinarian.
To give medications, the chicken should not be fed for 10 hours. Fasting will help you act more effectively on helminths. Hens and chicks are herded into a separate room with a concrete floor and fed with drugs. At this time, the chicken coop is disinfected. All feces are burned. After 8-12 days, repeated deworming is done in order to destroy the new worms that have appeared from the eggs.
Important!
After taking medications, carcasses should not be cut for 45 days and eggs should not be consumed for 2 weeks.
Traditional methods of fighting helminths
Traditional recipes are used in conjunction with drug treatment. They can also serve as preventive measures.
Chicken diet is diluted:
- pumpkin seeds;
- chopped garlic cloves;
- onions;
- rose hips;
- pomegranate seeds;
- lingonberries;
- wild garlic fruits;
- walnut;
- grated carrots;
- pine decoction.
It is better to feed chickens with chamomile infusion. Herbs are laid out in the chicken coop: wormwood, rosemary, wild rosemary, tansy. External parasites of chickens are afraid of these plants. Tar with vegetable oil helps in the fight against bedbugs. They wipe the cages and walls of the chicken coop with it.
Common helminthiasis in chickens
Trematodes
This problem is the result of the vital activity of the parasite Prosthogonimus ovatus. In laying hens it is localized in the oviduct, and in chickens it is found in the bursa of Fabricius.
A bird becomes infected when it eats the intermediate hosts (shellfish) that cause the problem. Pathology more often makes itself felt when birds have free access to natural bodies of water.
The disease is more severe in adult chickens.
The fact that a laying hen has trematodosis can be indicated by defective eggs received from her - irregular in shape, without a shell or yolk, with a thin shell. The worst thing that happens to laying hens is that the oviduct ruptures, which naturally leads to the cessation of egg laying.
Stages of pathology:
- There are no external signs of illness. The bird is behaving normally and eating food well. The reasons for suspicion of invasion are eggs with very thin shells and a sharp decrease in the level of egg production in laying hens and the growth rate in young animals. The duration of the stage is up to 30 days. This moment is determined by the immune status and external conditions.
- At this stage, accompanying pathology includes weak or absent appetite, unsteady gait, and enlarged abdomen. An affected chicken may not leave the nest for a long time and may not lay eggs. The duration of the stage is about a week.
- In this case, the disease manifests itself as a sharp deterioration in the bird’s condition, hyperthermia, and reluctance to eat. The departure of the problem individual occurs approximately on the fourth day (counted from the beginning of stage 3).
Ways to combat worms in chickens
The main preventive measure is to avoid walking after rain and in the morning until the dew disappears.
Effective drug treatment has not yet been developed. Immediately after the bird is infected, a short-term positive effect is observed after using Fenbendazole .
Echinostomatiasis
This parasitic disease is also provoked by trematodes, but belonging to the family Echinostomatidae.
Once in the host's body, the parasites are localized in the intestines. In chickens, the disease is rarely diagnosed. The life cycle of the parasite occurs with the participation of an intermediate host.
External and internal manifestations of the disease:
- Intestinal mucosa damaged by trematodes;
- increased secretion of juice;
- poultry sensitization;
- poor appetite or refusal to feed;
- constant thirst, due to which the bird does not leave the drinking bowl;
- loss of live weight;
- deterioration of productive qualities.
In order to make an intravital diagnosis, feces are studied.
Ways to combat worms in chickens
To prevent an outbreak of the disease, you should constantly keep drinking bowls clean and limit (exclude) access to walking areas.
Veterinary drugs used: Niclosamide and Praziquantel . When the course of drug treatment is completed, the poultry house is disinfected.
Nocotilidosis
Trematodes of this group are caused by Notocotylus attenuatus. We are talking about worms that parasitize in the rectum and cecum of the intestine. Flukes can be found in small bodies of water or large puddles, where they are carried by wild birds. During the life of worms, the gastrointestinal mucosa is disrupted. Damage becomes a gateway for infectious pathogens.
The fact that the bird is severely affected by flukes is indicated by a very weak and completely absent appetite, stunting due to low average daily gain in live weight. Many chickens die.
The diagnosis is made in laboratory conditions. The object of study is droppings or dead birds.
Ways to combat worms in chickens
Water sources that cause infection of birds are quarantined for 12 months. Treatment is based on the use of anthelmintic drugs, for example, Nicloamid. Mandatory measures include disinfection of litter and disinfection of the chicken coop.
Cestodoses Rayetinosis
This is a disease caused by the cestodes Raillietina echinobothrida. The culprits of the problem populate the small intestine. Their size does not exceed 25 cm. The life cycle of cestodes includes a stage with an intermediate host - ants.
The disease often makes itself felt in the spring and summer. In winter, the diagnosis is rarely confirmed. Due to the mechanical effect of parasites on the gastrointestinal mucosa, digestion is disrupted. Add to this toxicosis.
Pathology in young animals occurs predominantly in an acute form, in which lethargy, low mobility, and constant thirst are noted. This picture is often accompanied by convulsions and paralysis of the wings.
Ways to combat worms in chickens
Prevention is based on:
- Allocating each poultry technological group its own premises.
- Daily exercise - birds staying on a walking area or in an aviary.
- 2 times annual deworming.
Problematic individuals are treated with Bithionol . The drug is given twice at 4-day intervals.
Heteracosis
The provocateur of this disease is the parasite Heterakis gallinarum, or rather its eggs, which end up in the feed and then into the bird’s body. Symptoms: passivity, weak appetite or refusal to feed, diarrhea. The gastrointestinal mucosa suffers from the parasite.
Control measures. In disadvantaged areas, it is recommended to keep chickens of different age groups separately.
The bird is treated with Piperazine . In order to prevent a second wave of the disease, the poultry house is disinfected and the litter is subjected to biothermal treatment.
What drugs are used to “drive” worms from chickens?
Disinfection of the chicken coop
Cleaning of the chicken room is done once a year. If infection occurs, all birds are temporarily transferred to another room.
- Shoes are washed before entering the room.
- The walls of the chicken coop are covered with lime.
- All food and droppings are removed and burned.
- Walls and floors are washed with apple cider vinegar solution.
- Treat walls, floors, cracks with Formalin, Virocide, Glutex, bleach. Dust is used for the same purposes. All products are toxic, so wear gloves and a face mask.
Substances for spraying
Neocidol 5% is sprayed on the surface, in the cracks. No need to rinse off. For 50 sq. m. 2.5 l of solution.
Chlorophos 2%, 200 g of substance per bucket of water. Stir thoroughly and spray on the walls and floor. After a day, wash it off.
Delta Zone is designed against bedbugs. Per liter of water 5 ml of product.
Agran is used to kill bedbugs. 5 ml of product per 500 ml of water. When the surfaces are dry, the chicken coop is ventilated. The drug acts gradually.
Attention!
All substances are toxic, they should not get into poultry feed, and after treatment, do not house chickens for more than a day.
Harm and danger
If we talk about the dangers of this mite for the health of chickens, then it can cause the main damage to the productivity of these birds. Under the influence of feather eaters, the chicken’s body is greatly weakened and is unable to function normally. The egg production of birds decreases by an average of 10%. Chickens grow much slower than usual, while their sexual development is greatly slowed down and maturity occurs much later.
Decorative breeds suffer primarily aesthetically, since the structure of the plumage is disrupted and baldness appears. Affected feathers become dull.
Find out how to get rid of worms in chickens.
Unprotected areas of skin appear on the chicken's body, which are easily affected by infections. The skin becomes covered with wounds in which dirt accumulates and creates a favorable environment for the proliferation of microorganisms. As a result, in addition to being affected by the bird eater, the laying hen begins to suffer from other, no less dangerous, diseases.
How to deal with beetles
Having sensed the parasite, the birds try to cure themselves. But no matter how hard they try, it is impossible to rid chickens of ticks without human intervention.
It is necessary to begin the fight against beetles from the moment the first signs of their appearance in the chicken coop are detected. The infected individual must be immediately removed from the rest, and healthy chickens must be treated with insecticides. The poultry house is thoroughly cleaned and disinfected; in addition, surfaces can be treated with a blowtorch or steam.
In parallel with preventive work among healthy livestock, therapeutic measures are carried out for sick birds. In order to get rid of parasites, chemicals or folk remedies are often used.
Did you know? Period is dangerous not only for birds, but also for people. This tick can be a carrier of typhus or salmonellosis, and can also cause allergies. Its bites cause severe itching, which can lead to swelling.
Chemicals
Using chemical repellents is a very effective method. In every veterinary pharmacy you can find a lot of remedies for parasites. These poisons affect the nervous system of pests, which leads to their rapid death, without affecting the body of birds.
To make the use of drugs more effective, the following rules must be followed:
- Preparations in the form of drops should be applied to the withers so that the chicken cannot reach the feathers and get poisoned. Ticks die in a couple of minutes, so tying the beak can be another way to protect the chicken.
- Sprays are sprayed at a distance of 15 cm. You can protect the bird’s eyes from getting the medicine by covering its head with a cloth.
- The action of all drugs is aimed at destroying adult insects, but does not affect their eggs. In this regard, the procedure for destroying ticks must be repeated after 7–10 days. If you ignore it, then after two weeks the chicken will again suffer from parasites.
Important! Chemical preparations are too toxic and are not suitable for chickens, so for their fragile bodies it is worth choosing more gentle means.
Insecticides
As for such drugs, store shelves are now full of various products, but the most popular and accessible are the following:
- Nyuda is a human preparation in the form of a spray for removing lice. It has an equally effective effect on birds. Its price is quite high, and therefore it is most often used for processing small numbers of livestock.
- “Butox” is good at removing various types of insects. Produced in the form of ampoules. The product should be diluted in a ratio of 1 ml of medication per 1.5 liters of water. It is applied to feathers by spraying and is also used to treat poultry houses.
- "Frontline" is sold in both drop and spray form. Only harms adult ticks. Subsequent treatment is carried out a week later.
- “Insectol” - with this product, the chicken is treated with areas under the tail and wings, spraying the medication in an amount of 0.4 ml until the feathers are slightly moistened.
- “Arpalit” is a ready-made spray for complete treatment of poultry, which will protect the laying hen from further infection.
We recommend reading: Plant roses in well-lit areas
Disinfectants
Disinfection of birds is mandatory when feather eaters appear. Conventional means will not help to exterminate ticks; the desired effect can only be achieved thanks to those drugs that react in combination with water:
- “Butox” is an ampoule preparation against ticks and other parasitic insects. To treat one chicken, you will need one ampoule. The drug penetrates the skin and is eliminated from the body through the digestive system, which produces a complex effect on a number of parasites. Diluted with water in a 1:1 ratio.
- "Entomozan" - used for processing chickens. Before the procedure, collect all the eggs in the chicken coop, and then irrigate the birds with a solution of the drug and water (5 ml of Entomozan per 1 liter of water). Repeated treatment is carried out after 9 days.
- "Neostomozan" - the drug is used in the form of an emulsion. It is formed as a result of the reaction of medication and water. For chickens, it will be enough to mix 1.5 ml of solution with 10 liters of water. The liquid is poured into a spray bottle and sprayed on the bird.
- “Tsifox” - this drug is used to treat specific areas where ticks accumulate. The solution is prepared at the rate of 10 ml of the drug per 5 liters of water. After 12 hours from the time of treatment, the drug should be washed off with a damp cloth and soapy water.
Repellents
There are also a number of drugs that have a repellent rather than lethal effect on parasites. This is a fairly effective prevention for healthy chickens, especially if there is already an infected individual in the population. The most used drugs to eliminate the disease are the following:
- "Frontline" is used as a drug against ticks in dogs, but is also suitable for poultry. Quite an effective product and at the same time non-toxic. The drug is applied to the withers. Its effect lasts for several weeks.
- “Leopard” is used to destroy various types of parasites not only in animals, but also in birds. The product should be applied with a pipette to the bird’s neck, the recommended dose is 1.4 ml. This product is also used to treat roosts against pests by spraying medication.
- "Vitomax" - comes in the form of a spray, has a low cost. It is better to spray the product starting from the tail at a distance of 30 cm until the plumage is slightly moistened. The spray should penetrate the skin, but be careful not to let it get into your eyes.
Folk remedies
The abundance of chemicals allows you to quickly get rid of the periodontal beetle, although you can refuse them, since the pest can be removed using more environmentally friendly, and most importantly, cheaper, means.
Herbs
In our fields and gardens there are many different kinds of herbs that can save the chicken coop from feather eaters. The most repellent plants for these ticks are wormwood, chamomile, tansy and wild rosemary. All these herbs are dried and ground, after which the powder is scattered on the litter. This will serve as an excellent preventative against chicken fleas.
Another way to get rid of ticks is powder made from blackberry and hellebore branches. This mixture is sprinkled on the bird, which helps an already infected chicken get rid of parasites. But this product carries some danger for weakened chickens; in this case, you need to dilute the product with water (2 g per 0.5 l).
Decoctions and infusions
Herbal decoctions can be treated no less effectively than medications.
For example, chamomile infusion is brewed like strong tea, and this remedy is rubbed into the affected areas of the skin for a week. You can also use this method to eliminate illness in chickens.
We recommend reading: The benefits of cherry juice
It is also recommended to brew a solution of tansy and wormwood, which is then used to wash shelves, walls, feeders and drinkers in the poultry house. To do this, you need to brew one of the plants in boiling water in a 1:1 ratio and let it brew overnight.
Ash
Ash has proven itself very good in the fight against chicken fleas. Its mixture with sand removes parasites very quickly.
In order to prepare this remedy, you will need ash and sand in equal proportions. These ingredients are mixed and placed in a container that is installed at the entrance to the chicken coop. It is better to have several such baths, then it will be easier for laying hens to bathe without interfering with each other.
Insects cannot tolerate such procedures and die or run away.
You can also make some kind of cream from the ash by adding vinegar or kerosene to it. This medicine is applied to the chicken and left until the effect occurs. The air supply to the parasites is blocked and they die. But this procedure can only be done with adult chickens.
Prevention measures
It is better to prevent a disease than to treat it. Prevention rules:
- Wash your shoes and hands before and after visiting the chicken coop.
- Remove litter in a timely manner and monitor its consistency.
- Change the flooring regularly.
- Inspect chickens and disinfect chicken premises.
- Monitor the air humidity in the chicken coop.
- Prevent contact between poultry and wild birds.
- Destroy rodents.
- For prevention, give drugs against worms, especially to new individuals.
Parasites cause significant damage in poultry farming. It is difficult to get rid of bedbugs and ticks if the shelter has not been completely disinfected. The insect population will recover quickly. In order not to waste time and money on treatment, preventive measures are taken that will protect chickens from parasites and subsequent complications after infection.
How to remove worms from chickens
If you notice at least one of the symptoms in your patients that indicates an invasion, immediately begin treatment. Otherwise, the risk of mortality of the entire livestock is high.
Antiparasitic drugs
There are many drugs available to treat worms in laying hens. When choosing them, you should be guided by the symptoms of poultry, which will help identify the pathogen. According to experts, they have proven themselves well:
- "Febtal" - effective in the fight against roundworms, amidostoma nematodes, heterakis and threadworms. The therapeutic course involves taking a medicinal solution for three days. It is given in a dose of 0.45 g per 10 kg of bird weight. On large farms, they are limited to calculating the total weight of chickens. The granules are simply dissolved in drinking water or mixed into wet food.
- “Phenothiazine” is recommended for blocking the vital activity of roundworms and heterakises, to which chickens are very vulnerable. Therapeutic as well as preventive courses are designed for three days of taking the medicine. It is added to wet mash in a ratio of 1:15.
- "Avatek" ― is popular among veterinarians because it is a broad-spectrum drug. But the anthelmintic effect can be achieved only after taking the medicine for a week. It is most often used on poultry farms, dissolving 500 g of the product in a ton of drinking water.
- “Filixan” is considered among veterinarians to be the safest drug with good effectiveness in the fight against causative agents of cestosis. Due to its mild toxicity, it is prescribed for preventive purposes for young animals. Therapy, as well as prevention, is carried out by giving the birds an anthelmintic solution for three days. If desired, the product can be added to the mash, the main thing is that each patient swallows at least 0.3 g of the drug.
- "Levamisole" ― is popular due to its wide spectrum of action. It is used intramuscularly or orally for 3 days in a proportion of 2.5 ml for each individual.
- "Piperazine" ― intended for the destruction of roundworms and amidostoma nematodes. The course of treatment is carried out in a single dose (1 tablet for each chicken). After a month, it is recommended to repeat the procedure for preventive purposes.
- "Pirantel" - effective against roundworms and nematode worms. Treatment consists of a single dose of medication (1 tablet for every kilogram of live weight). For prevention purposes, it is recommended to repeat the course twice at weekly intervals.
Did you know? Worms, depending on their quantity, can drink about 0.5 liters of blood from the owner every day.
Folk remedies
If for some reason drug treatment is not suitable for your animal, you can try traditional anthelmintic remedies. Of these, the following are worthy of attention:
- garlic - recommended as a dietary supplement at every feeding (portions should be moderate);
- leeks - chopped, added to mash at each feeding;
- pumpkin seeds ― have an anthelmintic effect due to the cucurbitins they contain (it is enough to mix them into the feed; it is advisable to grind them for young animals);
- rosehip - used in crushed form as an anthelmintic, it is recommended to add it to wet food;
- wild garlic and lingonberry fruits - unlimited quantities of berries are offered to chickens, they peck them with pleasure;
- walnut kernels;
- a decoction of medicinal chamomile flowers (recommended for small chickens);
- sorrel leaves;
- a decoction of coniferous plants (bark and branches are used);
- pomegranate seeds.
We recommend reading: Why does a cow have salted milk if she is not pregnant, salted milk before and after calving: causes and treatment
Experienced poultry farmers advise combining healthy products when preparing feed. This will increase the chances of expelling parasites.
Important! Less often, chickens that are kept in a closed enclosure suffer from helminthic infestations, provided that access to their food from wild birds is excluded.